The Technology Behind How Smoke Detectors Work: Simple but Lifesaving
Smoke detectors are one of the most important devices in a fire protection system. Despite their small size and seemingly simple appearance, the technology behind them is highly sophisticated and has been proven to save lives in emergency situations.
This device works by detecting smoke particles in the air, which are an early indication of a fire. By detecting smoke early, smoke detectors provide more time for evacuation and fire suppression before it spreads.
In this article, we will explain the various technologies used in smoke detectors as well as the working principles of each type commonly used in various buildings.
The Technology Behind How Smoke Detectors Work
Smoke detectors generally use two main types of technology: ionization and photoelectric. In addition, there are also smoke detector with additional features for specific needs. Each has its own advantages depending on the type of fire being detected.
Ionization Smoke Detectors Work
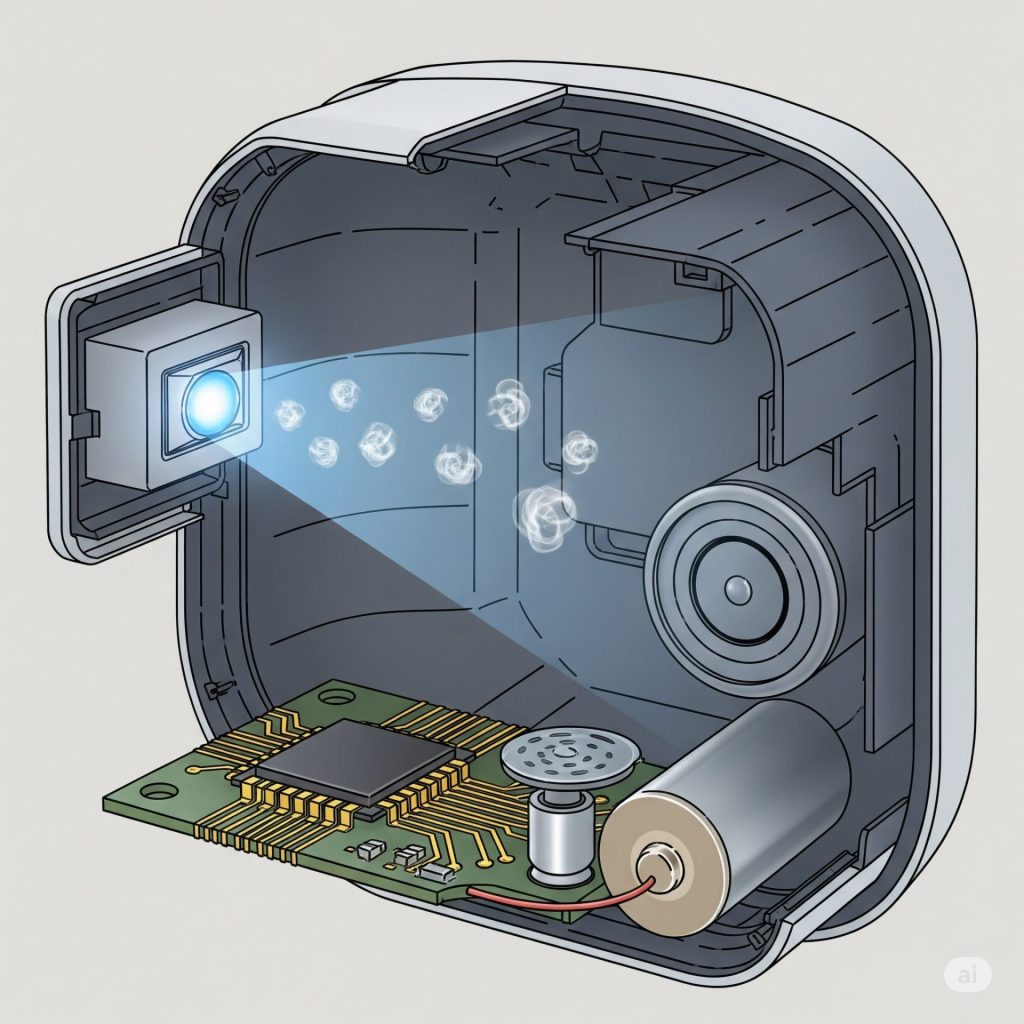
Ionization smoke detectors use radioactive materials such as Americium-241 to create an electric field between two metal plates.
This field produces a steady flow of ions. When smoke enters the detection chamber, smoke particles disrupt this ion flow. This disruption causes a decrease in electrical current, which then triggers an alarm.
This type of smoke detector is very effective in detecting fast-moving fires with large flames (flaming fires). Therefore, ionization detectors are often used in areas at high risk of rapidly spreading fires.
Photoelectric Smoke Detectors Work
Unlike ionization, photoelectric smoke detectors operate on the principle of light scattering. Inside the detection chamber, light from an infrared LED is emitted in a straight line.
When there’s no smoke, this light doesn’t hit the light sensor (photodetector). However, when smoke enters, its particles scatter the light toward the sensor, triggering the alarm system.
This technology is more sensitive to thick smoke from smoldering fires, such as burning furniture or slowly burning wires. Therefore, this type is often recommended for environments House or office space.
Smoke Detector with Additional Features
To improve the accuracy and detection range, smoke detectors with additional features have also been developed, including:
- Dual-Sensor Smoke Detector
Combining ionization and photoelectric technologies in a single device, this combination allows for more effective detection of various types of fires and reduces the risk of false alarms.
- Beam Smoke Detector
It uses an infrared beam that is emitted from one side of the room to the other. If smoke crosses this beam’s path, the sensor triggers an alarm. It’s suitable for use in large areas such as halls, warehouses, or factories.
- Aspirating Smoke Detector (ASD)
It uses a pipe system to draw air from the room to an ultra-sensitive sensor (nephelometer). This detector is capable of detecting very small smoke particles and providing early warning. It is commonly used in server rooms, museums, or valuable archives.
In general, smoke detectors operate by detecting changes in the environment caused by smoke, either through electrical disturbances (ionization) or light scattering (photoelectric). This technology enables early detection, which is crucial for preventing fires from spreading and saving lives and assets.
To implement a reliable smoke detection system, it’s crucial to choose the right detector type for the room’s characteristics and the fire risk. As experienced fire protection contractors at Adiwarna, we are ready to help you design and install the right smoke detection system that meets the highest safety standards.
By understanding how smoke detectors work and choosing the right technology, you not only protect your building but also the people inside. Don’t wait until a fire breaks out; investing in a good detection system is a wise move for long-term protection.







